For Stretched, Ripped, and Torn Earlobes
How does the earlobe get damaged?
Earlobes are made entirely of soft tissue, and wearing earrings makes the lobes susceptible to damage. This can result from wearing heavy earrings, earrings accidentally being pulled, or intentional stretching from wearing gauged earrings. Earrings may get caught in clothing or a comb, or pulled by a brush. A skilled plastic surgeon can correct damage to the lobe, and with continued care, the lobe can often be re-pierced to accept earrings after a few weeks of healing.
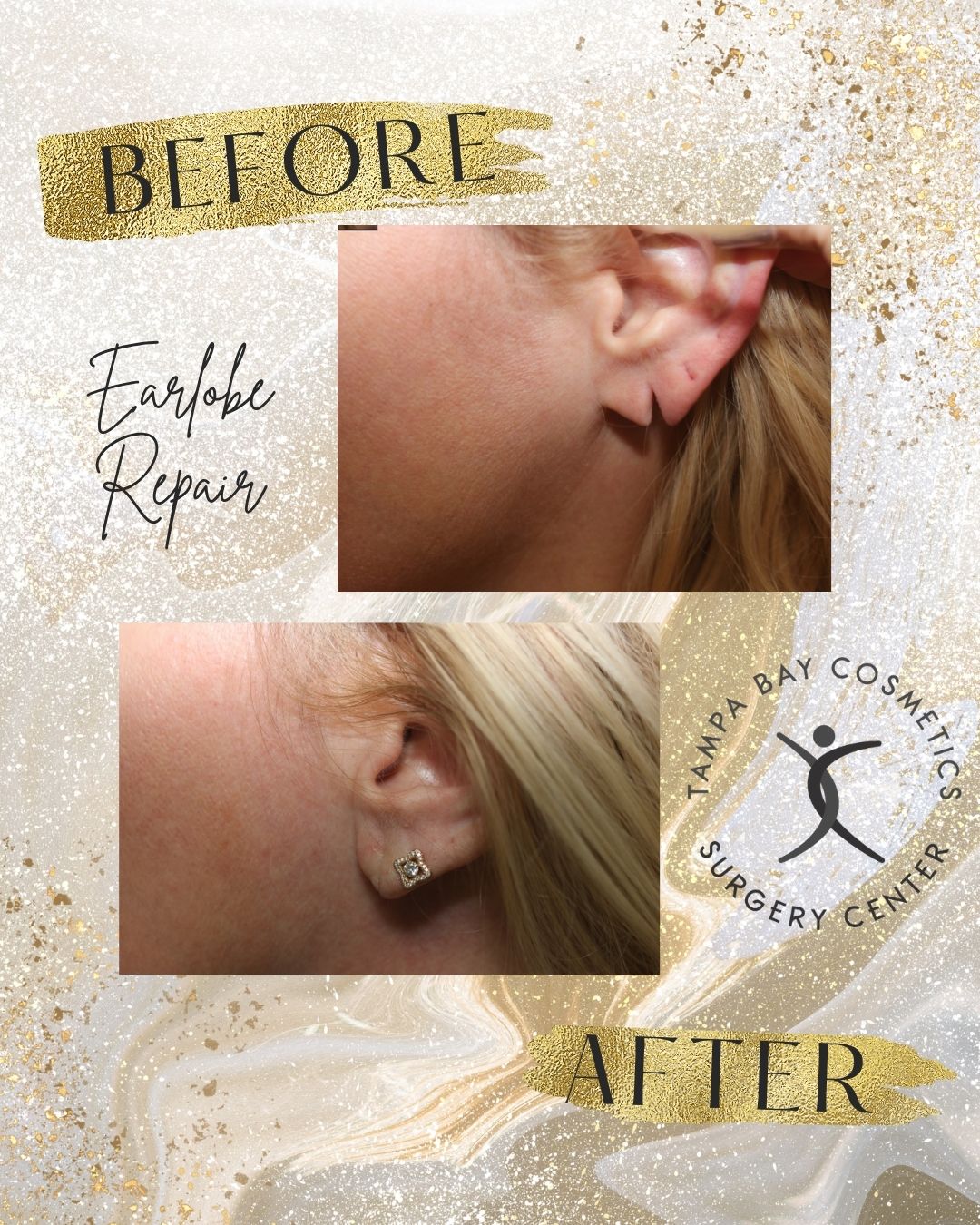
Split Earlobe Repair
Split earlobes are usually caused by prolonged use of heavy earrings or accidental pulling and tugging on an earring by a child or during hair combing. When earrings are too heavy, ear piercings tend to stretch and elongate because the entire weight of the earring is transferred to the bottom of the ear piercing via a thin hook or clasp. As a result, a high pound-to-square-inch force is applied to the earlobe. Stretching can be partial or full, with full stretching resulting in a complete split.
When done properly, the results include a smoother, more even scar with less chance of indentation, preserving a viable lobe capable of bearing re-piercing and moderate weight.
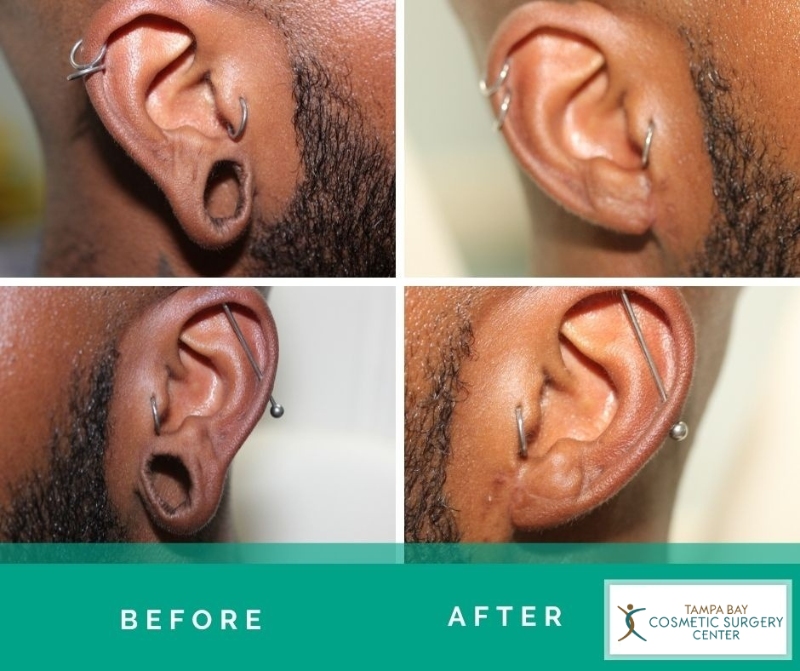
Gauged Earlobe Repair
Gauged earlobe stretching is the gradual expansion of a simple ear piercing to fit larger-sized plugs. Excessive stretching of earlobes by expanders known as gauges causes thinning and distortion of the earlobe tissues. The more severe the distortion, the more difficult it is to repair the gauged earlobe and restore it to a normal or near-normal shape. There is no single established technique for repairing gauged earlobes. The plastic surgeon relies on advanced plastic surgery knowledge and experience.
Earlobe Reduction
Some individuals are born with larger than average earlobes, which can cause self-consciousness. The correction considers size discrepancies or asymmetry and is modified accordingly, with the creation of an even and symmetrical result as the goal. Earlobe reduction is performed under local anesthesia, involves no downtime, and healing typically takes 6-7 days. Over-the-counter pain medication is usually adequate to manage any postoperative discomfort.
Repair of Earlobes with Stretched Holes
Stretching or elongation of the earlobe piercing results from wearing heavy earrings or accidental pulling by a child, catching on clothing, or sometimes during hair combing. The stretch may be large enough for studs to fall out. The best correction method is to completely close the stretched hole and re-pierce a few months later. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, with healing taking approximately one week and no downtime. The operation takes about 40 minutes per ear. Over-the-counter pain medication is sufficient to manage any postoperative discomfort.
Frequently Asked Questions About Earlobe Repair
Q: What causes earlobes to become stretched or torn?
A: Earlobes can become stretched or torn from wearing heavy earrings, accidental pulling or tugging, getting caught in clothing or hairbrushes, or from intentional gauging or stretching techniques.
Q: How long does it take to heal after earlobe repair surgery?
A: Healing typically takes about one week to 6-7 days, depending on the procedure, with most patients experiencing minimal downtime and manageable discomfort with over-the-counter pain medication.
Q: Can earlobes be re-pierced after repair?
A: Yes, after the earlobe has sufficiently healed—usually a few weeks following surgery—re-piercing is often possible, allowing patients to wear earrings again.
Q: Is earlobe repair surgery painful?
A: The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, so pain during surgery is minimal. Post-operative discomfort is generally mild and can be controlled with over-the-counter pain medication.
Q: Are there any risks or complications associated with earlobe repair?
A: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection, scarring, or asymmetry. However, choosing an experienced plastic surgeon and following post-operative care instructions can help minimize these risks.
